Diabetic Retinopathy Specialist
Comprehensive Eye Care
Monday-Thursday 9:00 AM–5:00PM
Friday 9:00 AM–4:00PM
Closed Saturday-Sunday
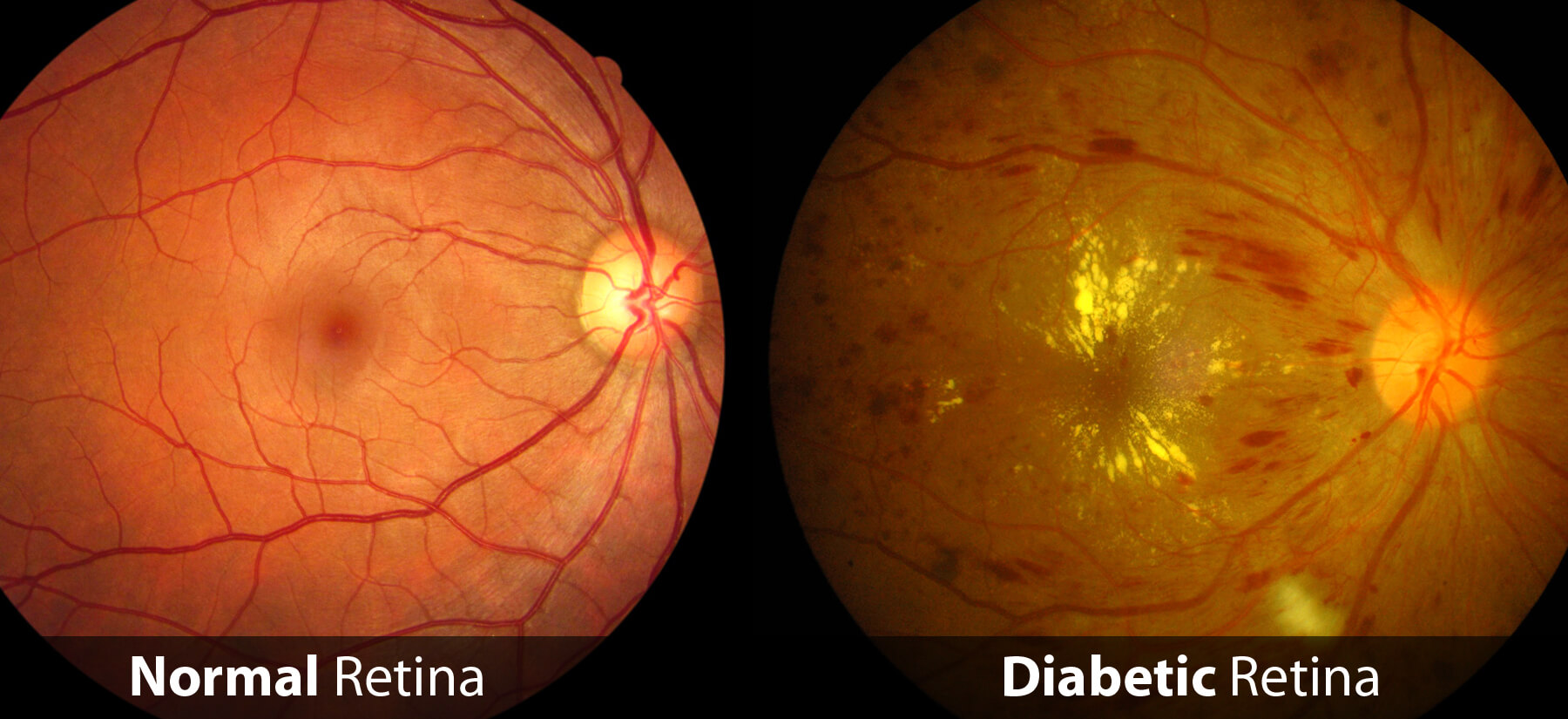
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetes is a disease that is caused by your body’s inability to produce insulin or inability to use the insulin you do produce to effectively control your blood sugar levels. All types of Diabetes can lead to damage of the blood vessels in your retina leading to bleeding, leaking fluid, or lack of blood flow. These findings can lead to reduced vision or even permanent vision loss.
Diabetic Retinopathy Q&A’s
WHAT IS NONPROLIFERATIVE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY?
The earliest stage of diabetic retinopathy is known as nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. With this condition, damaged blood vessels in the retina begin to leak small amounts of blood and other fluid into the eye.
Patients may also have deposits of cholesterol or other fats from the blood leak into the retina.
WHO IS AT GREATEST RISK OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY?
All people with diabetes are at risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. This is especially true if you have poor blood sugar control.
Your risk of diabetic retinopathy increases if your diabetes is accompanied by:
- Pregnancy
- Obesity
- High blood pressure
- High blood lipids
- People of African American, Hispanic, or Native American descent are also at greater risk.
How is Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosed?
Diabetic retinopathy can only be diagnosed with a comprehensive eye exam, which evaluates the health of the inside of your eye. Your doctor may use a dilated eye exam, retinal photography, or Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) to evaluate for clinical signs of Diabetic Retinopathy.
What is Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy?
When Diabetic Retinopathy becomes advanced and the retinal blood vessels become more significantly damaged, you can develop proliferative diabetic retinopathy. This condition occurs when new blood vessels grow, called neovascularization, to try to aid a damaged retina. Proliferative diabetic retinopathy can cause significant vision changes and can lead to retinal detachments and permanent vision loss.
How is diabetic retinopathy treated?
The most important tool to prevent or reduce the risk of diabetic retinopathy is to monitor and maintain your blood sugar. In early stages, retinal findings and vision changes can resolve after blood sugar is better controlled, but careful monitoring is necessary. If proliferative diabetic retinopathy develops, advanced treatments with a retina specialist will be necessary to try to preserve vision.
Whether you need a routine eye exam, specialty treatment, or want to explore our wide range of eyewear options, we are here to help.
FAQ about Diabetic Retinopathy
-
Diabetes damages retinal blood vessels due to high blood sugar, causing leaks, swelling, or blockages (diabetic retinopathy). This disrupts oxygen flow, triggering abnormal vessel growth. Left untreated, it leads to vision loss. Annual dilated eye exams detect early changes, even without symptoms.